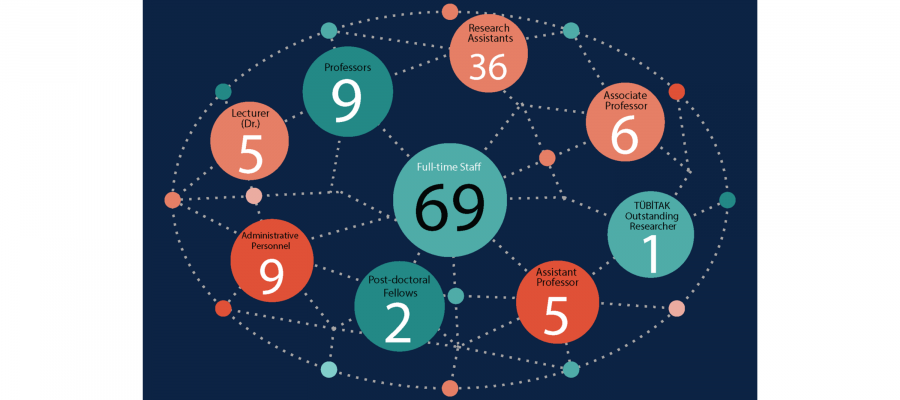
Announcements
Research News
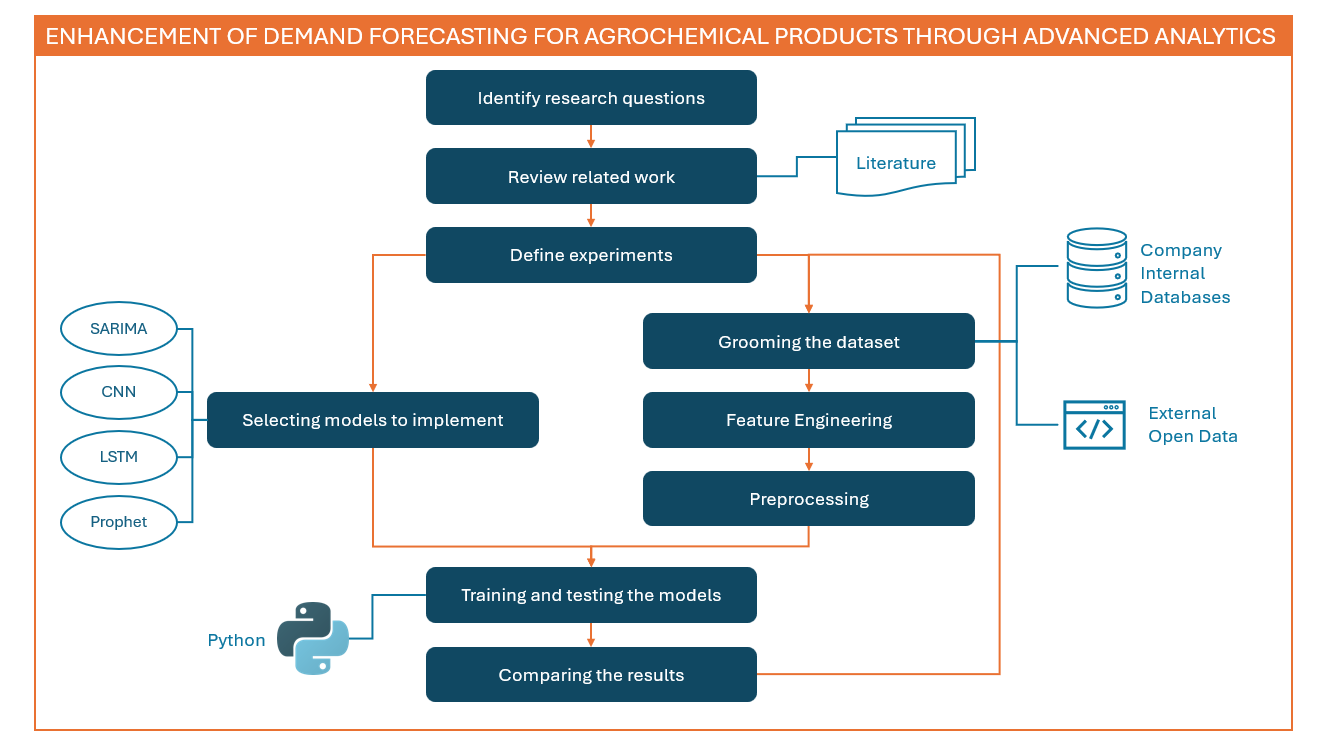
This thesis aims to improve demand forecast accuracy through the implementation of machine learning/deep learning applications. SARIMA, LSTM, CNN, and Prophet models are implemented to forecast demand. The models are trained and validated using forward-chaining cross validation method. It applies time series forecasting on a seasonal, unbalanced and intermittent dataset. The effects of selected exogenous indicators and aggregation-disaggregation approaches are examined for further improvement.
Date: 20.01.2026 / 14:30 Place: A-212
This thesis presents an integrated framework for AI-assisted BIM analytics and digital twin development to support indoor navigation and emergency evacuation. Revit-based BIM data are transformed into a unified pipeline by separating geometric representations from structured spatial information and integrated into a Unity-based digital twin. Real-time indoor pathfinding is enabled using the A* algorithm while considering physical evacuation constraints. A large language model (LLM) provides natural-language navigation instructions and supports context-aware user interaction. The system enables interactive visualization and testing and is evaluated through user studies, demonstrating a scalable and human-centred approach for BIM-based digital twin applications.
Date: 14.01.2026 / 14:15 Place: II-06

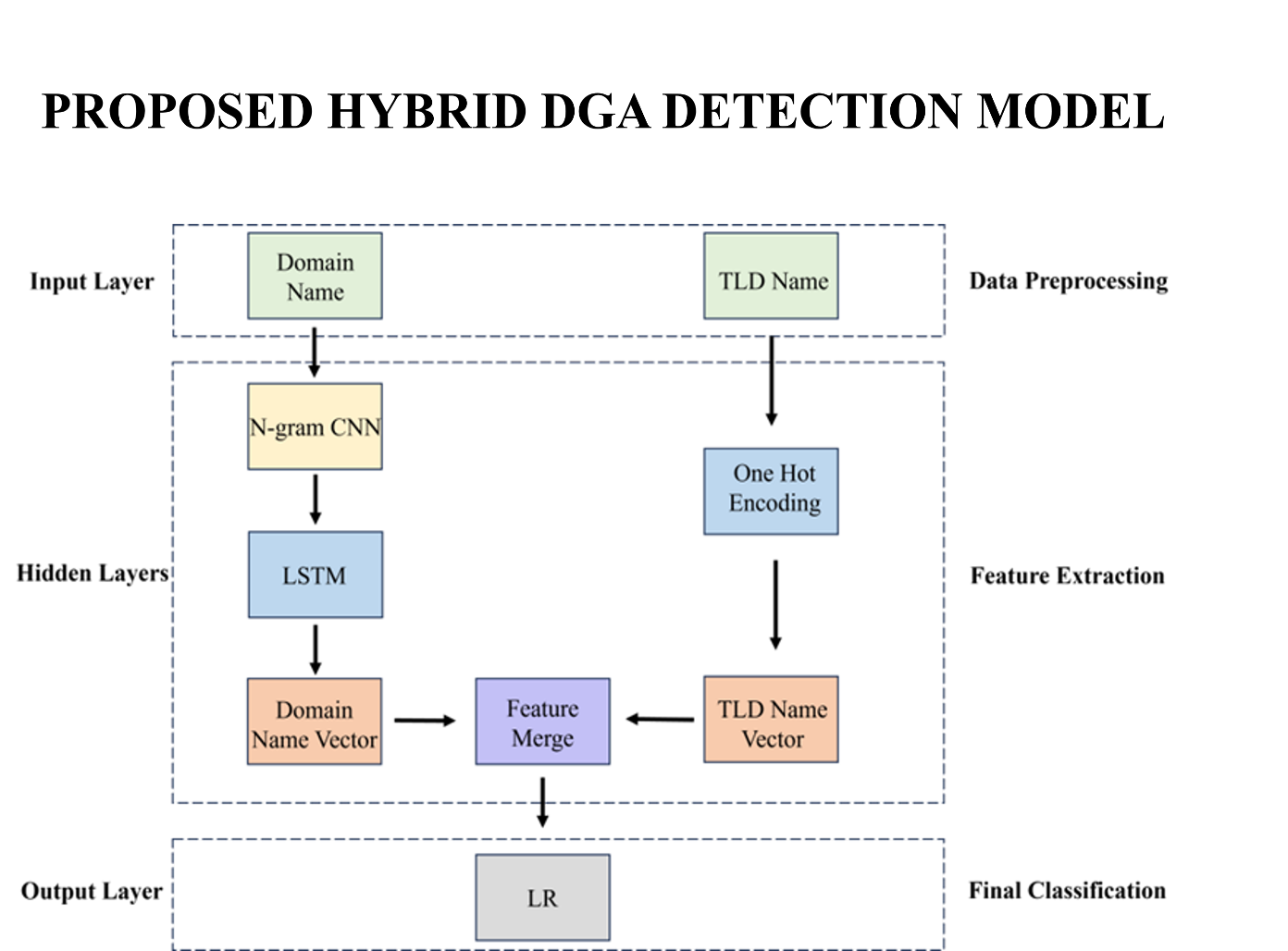
The problem of distinguishing legitimate domains from DGAs is an ongoing challenge. CTAs use DGAs to bypass traditional detection mechanisms like blacklisting or static signature-based solutions. Since blacklisting all DGA-generated domains is not possible, the automatic detection of DGAs remains a critical necessity. Despite years of research, modern malware continues to evolve, and this makes detection increasingly difficult. This thesis employes a hybrid framework that integrates CNN based n-gram learning and LSTM for automatic feature extraction and Logistic Regression (LR) for final classification. The model input is further enriched by Top-Level Domain (TLD) information in order to improve DGA detection.
Date: 16.01.2026 / 11:00 Place: Cisco Lab
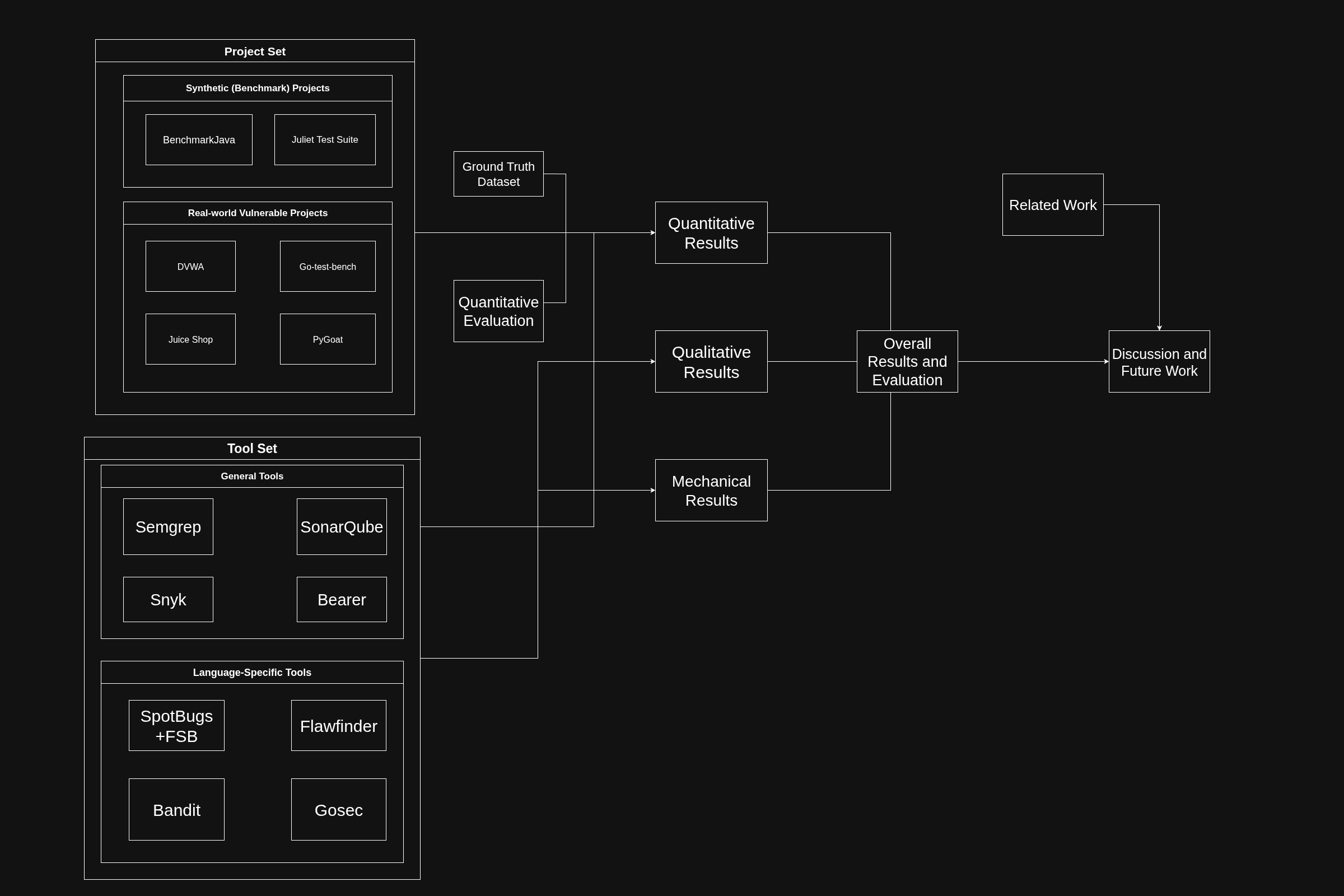
This thesis presents a systematic evaluation of Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools. Related studies mostly use synthetic codebases and per-vulnerability evaluation methods. In this study, both synthetic benchmarks and real-world intentionally vulnerable applications are tested against tools, along with per-issue evaluation. Conducted experiments measure various metrics and explain these results with reasons behind them. In addition to quantitative results, qualitative features and internal mechanisms of tools are examined to further explain results and observed performance differences. The results demonstrate the difference between evaluation models and tool effectivenes. Overall, thesis offers practical insights for SAST tool research and selection.
Date: 15.01.2026 / 10:00 Place: Cisco Lab
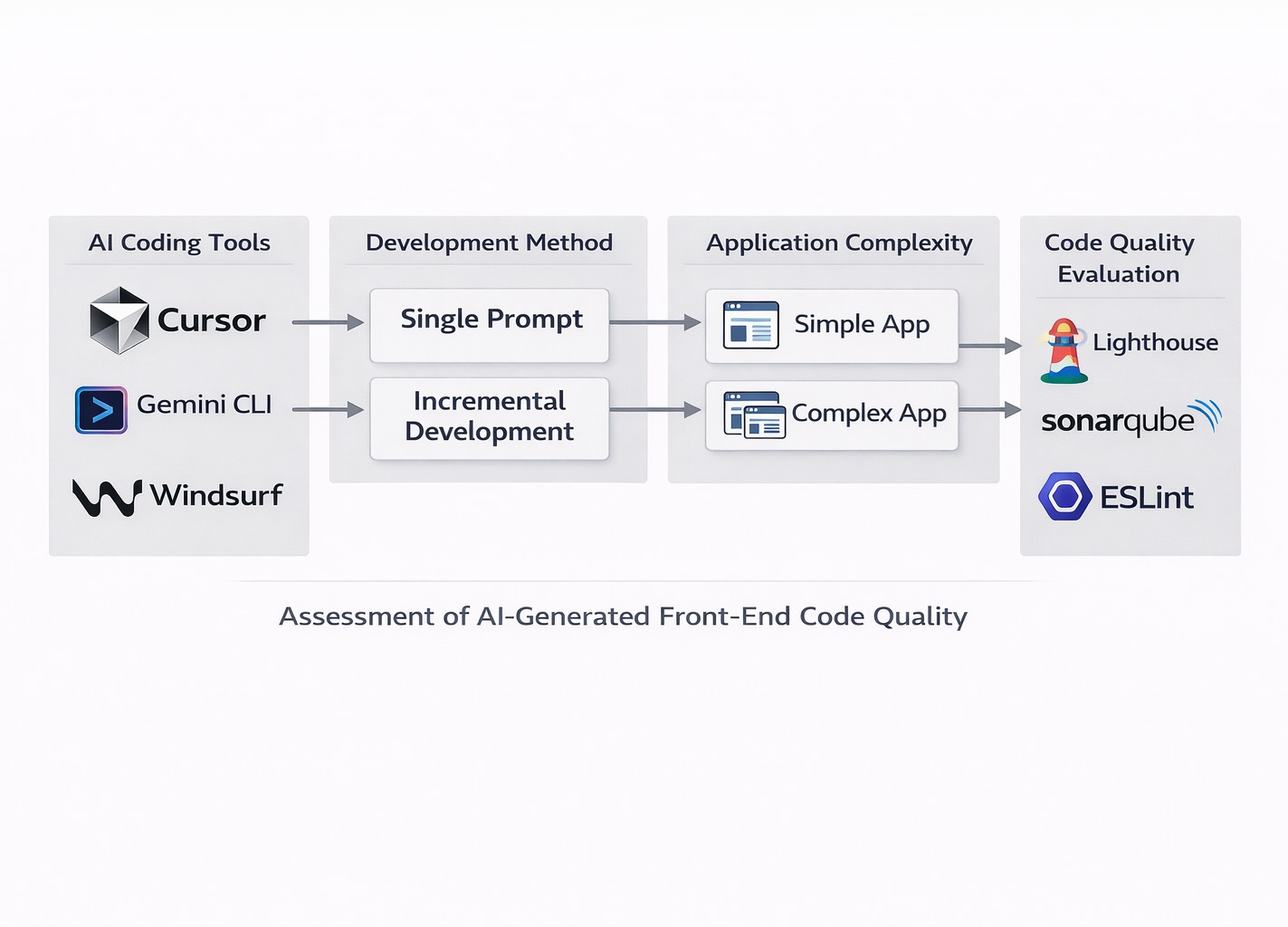
This thesis presents a comparative empirical evaluation of AI-generated front-end code quality. Three contemporary AI coding tools—Cursor, Gemini CLI, and Windsurf—are assessed through controlled experiments involving React and TypeScript applications of varying complexity. The study evaluates both single-prompt and incremental development approaches using industry-standard metrics, including Lighthouse, SonarQube, and ESLint. The findings demonstrate that while AI tools can generate functionally correct applications, code quality outcomes vary significantly depending on tool choice, development methodology, and application complexity. The results provide evidence-based guidance for selecting AI tools and workflows in modern front-end development.
Date: 20.01.2026 / 13:00 Place: A-212