Ph.D. Candidate: Mustafa Uğuz
Program: Information Systems
Date: 28.08.2024 / 14:00
Place: A-212
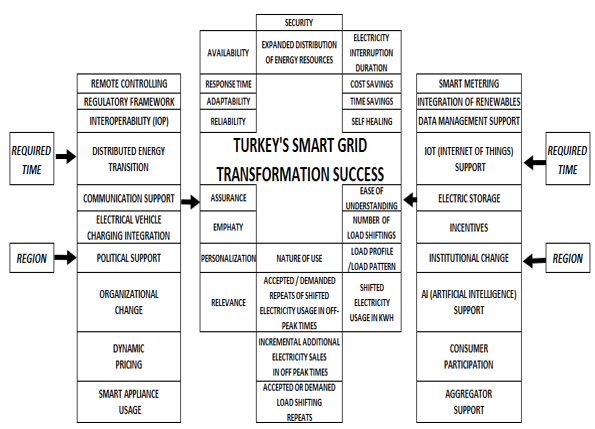
Abstract: The increasing world population has led to a significant rise in electricity demand, which traditional grids cannot meet. In response, the smart grid offers a promising solution to many issues within the existing electricity infrastructure. By integrating various information systems and technologies, the smart grid provides more efficient, cleaner, more reliable, and cost-effective electrical energy to all customers, contributing to the solution of an important global challenge. In Turkey Transitioning from the traditional grid to a smart grid necessitates the involvement of all related parties including governmental entities, regulators, electricity generators, consumers, exchangers, transmission, and distribution system operators, as well as IoT manufacturers. This study identifies and analyzes the parameters for the successful transformation from a traditional grid to a smart grid, with a particular focus on the case of Turkey. Through a comprehensive literature review , Delphi Analysis, expert views and surveys the study determines the dependent and independent variables of smart grid transformation success, examining the country's electricity grid institutions, stakeholders, and overall structure. The parameters of the successful transformation from traditional grid to smart grid in Turkey are determined and analyzed by a survey with the participation of 535 respondents from Turkish electricity ecosystem. The methodology developed in this study will be illuminating for the smart grid transformation of other countries as well.