Ph.D. Candidate: Zeliha Yıldırım
Program: Cognitive Science
Date: 13.01.2026 / 13:30
Place: A-212
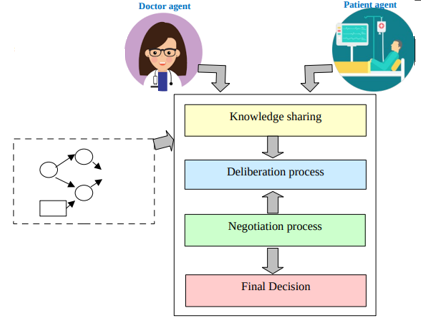
Abstract: Shared Decision-Making (SDM) is a patient-centered healthcare approach emphasizing patients as equal partners with physicians in a two-way information exchange. This dissertation introduces a novel framework, ID-SDM (Influence Diagram for Shared Decision-Making), based on Influence Diagrams (IDs) to model SDM computationally, reflecting the steps of the widely used conceptual framework, the Three‐Talk Model. In the proposed model, the physician’s and patient’s decision models are represented by separate IDs that capture their initial knowledge and preferences. The SDM interaction is then simulated using three fundamental node operations as its building blocks: (1) decision alternative transfer, (2) chance node transfer, and (3) preference node transfer. The model also leverages the Value of Evidence (VoE) metric to prioritize the most valuable information to be shared with the patient during clinical encounters. Illustrated using two demonstrative examples and a Graves’ Disease case study, ID-SDM simulates patient-clinician models, such as Paternalistic, Informed patient, professional-as-agent models, and SDM. Findings show that SDM requires fewer node transfers to reach the optimal decision of the perfect-information-sharing model compared to other clinician-patient relationship models. The Expected Number of Iterations decreases when both sides share more information upfront. Sensitivity analysis reveals that the optimal decision is highly sensitive to probabilistic input changes when patient utility weights are high. Lastly, the physician must assign more weight to the patient’s criteria to achieve the perfect-information-sharing model’s optimal decision.