Yavuzhan Çakır, Exploring The Genetic Landscape of Covid-19 Susceptibility Among Patients in Türkiye: an SNP Analysis
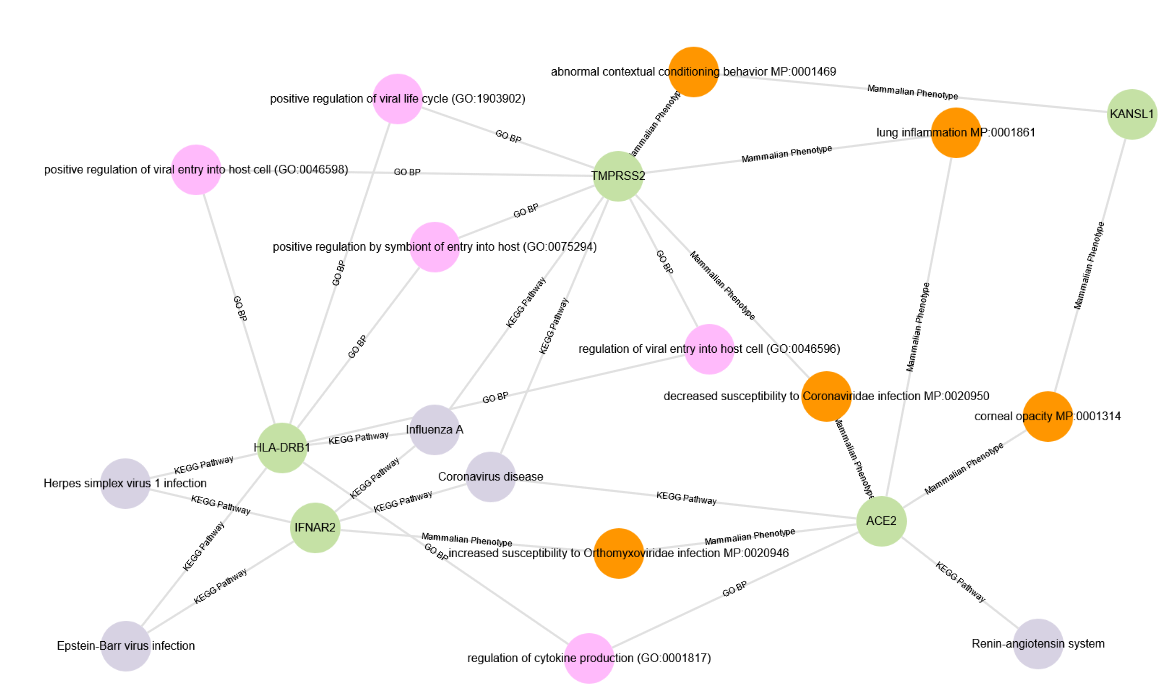
This study investigates the association between SNPs and COVID-19 susceptibility in the Turkish population, focusing on patients from Hacettepe University Hospital. Using NGS, we analyzed SNP data from various scientific publications, performing variant calling, linkage analysis, and statistical comparisons with non-Finnish European allele frequencies. Key findings indicate that certain variants have different frequencies compared to the European population, suggesting genetic predispositions affecting disease susceptibility in the Turkish population. Linkage disequilibrium analysis revealed strong correlations between specific genetic loci.
Date: 23.07.2024 / 15:00 Place: A-212