Kamran Karimov, Predicting the Primary Tissues of Cancers of Unknown Primary Using Machine Learning
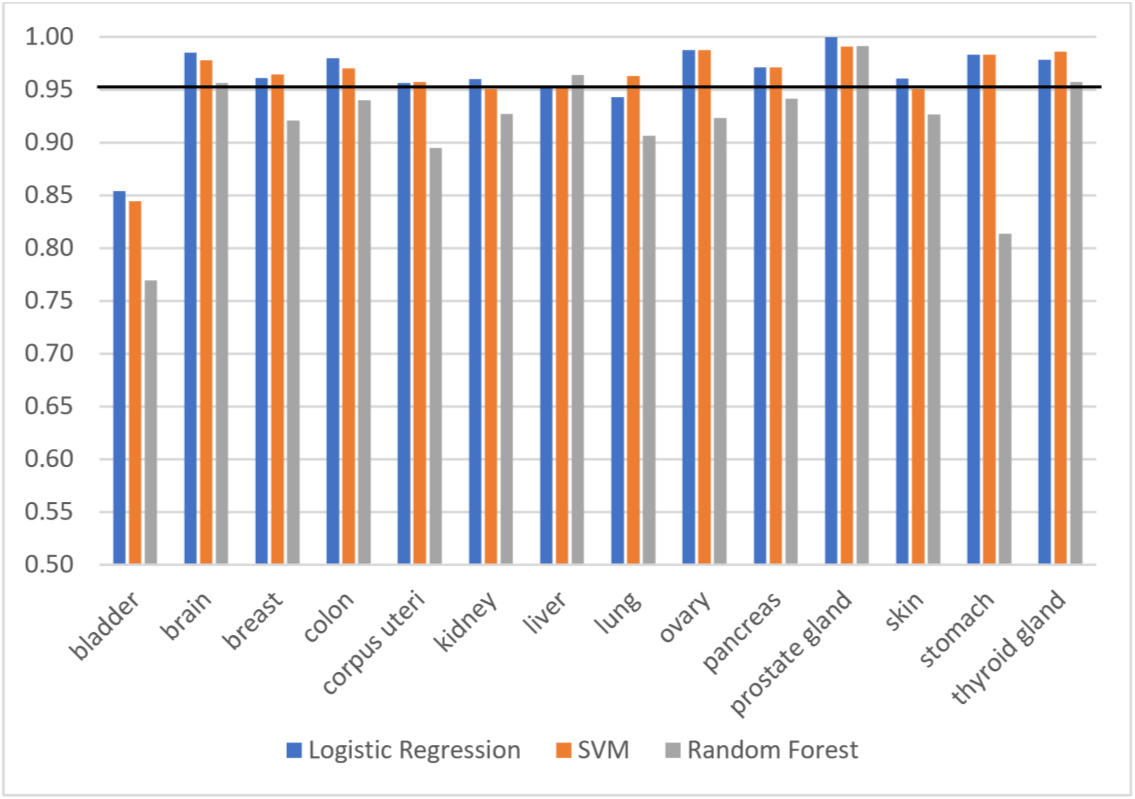
Cancers of unknown primary (CUP) pose treatment challenges due to unidentified primary sites, affecting survival rates significantly. Traditional methods falter in pinpointing origins. Gene expression-based studies offer promise; machine learning models trained on annotated cancer data achieve remarkable accuracy, surpassing conventional methods. Our study, utilizing three machine learning models trained on TCGA data, attained competitive accuracy, around 96%.
Date: 18.01.2024 / 11:00 Place: A-108