Batuhan Karataş, Negative Dependencies and Intervention Effects in Turkish
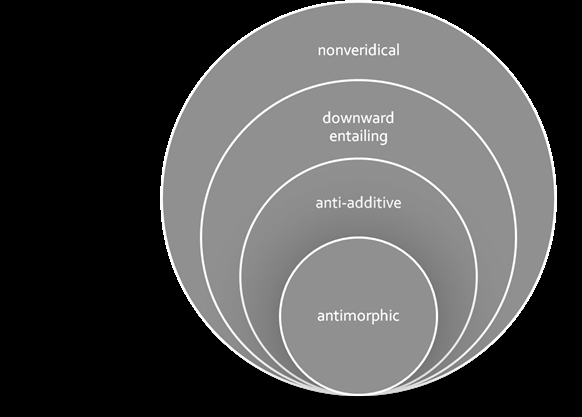
There are two goals of the thesis: (i) to understand the descriptive properties of the so-called negative dependencies in Turkish, which are expressions that basically require the presence of a negative-like element or environment to be well-formed; and (ii) to understand the so-called intervention effects on negative dependencies, where the term refers to the anti-licensing of negative dependencies in an otherwise adequate structure due to the presence of some elements (e.g. conjunction, universal quantifier, etc.).
Date: 06.09.2024 / 14:00 Place: A-212