Yasin Afşin, Automatic Evaluation of Mobile Health Applications According to Persuasive System Design Principles and Mobile Application Rating Scale
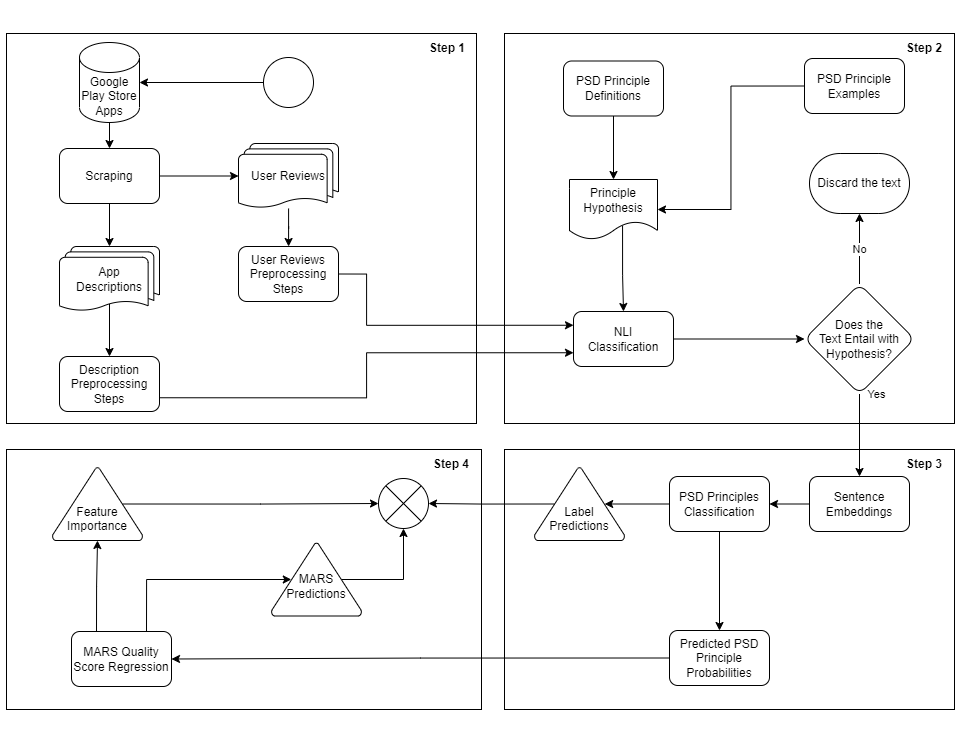
This thesis proposes automatic evaluation techniques to assess mobile health applications as alternatives to manual methods. It utilizes large language models to classify applications' employed Persuasive System Design (PSD) principles from collected user reviews and application descriptions. Mobile Application Rating Scale (MARS) scores are predicted with regression models trained on classification probabilities that are enriched with additional descriptive data. The study’s proposed techniques outperform baseline models, while feature importance scores show that PSD principles have significant contributions to quality predictions of mobile applications.
Date: 20.06.2023 / 14:00 Place: A-212