Gizem Kaya, Enhancement of Demand Forecasting for Agrochemical Products Through Advanced Analytics
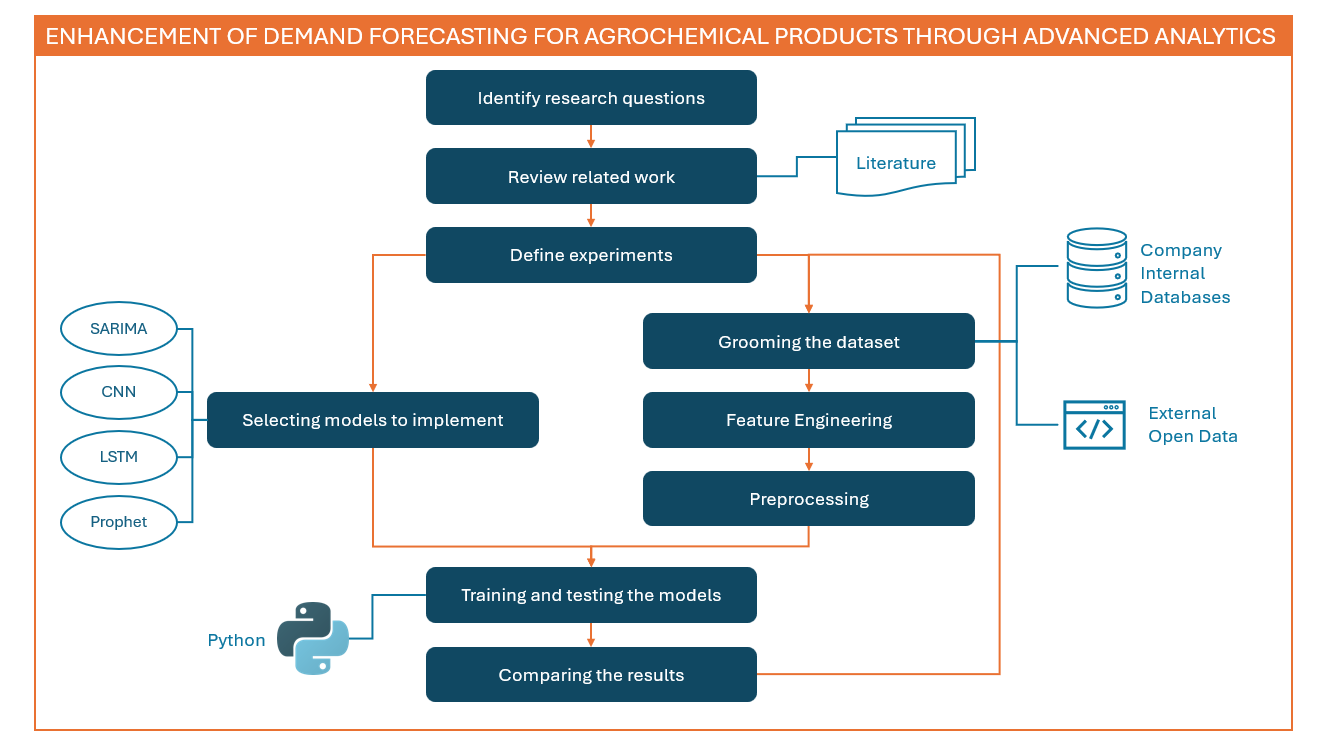
This thesis aims to improve demand forecast accuracy through the implementation of machine learning/deep learning applications. SARIMA, LSTM, CNN, and Prophet models are implemented to forecast demand. The models are trained and validated using forward-chaining cross validation method. It applies time series forecasting on a seasonal, unbalanced and intermittent dataset. The effects of selected exogenous indicators and aggregation-disaggregation approaches are examined for further improvement.
Date: 20.01.2026 / 14:30 Place: A-212