Esin Yiğit, Prediction of Surgical Durations Using Machine Learning Methods
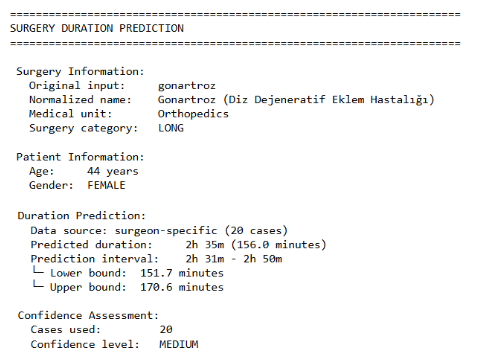
Predicting surgical case durations accurately is essential for operating room scheduling and resource management of healthcare facilities. While everything relies on technology recently, enabling a system that predicts surgical durations using machine learning enhances accuracy, decreases workload of the healthcare personnel and increases patient satisfaction eventually. Using RFID-derived data to develop this machine learning model is more precise because the data source is not manually recorded. By dividing the available surgical data into three as short, medium and long, predictions are made by giving an estimation interval and the results are coherent with the literature according to the error rates.
Date: 13.01.2026 / 10:00 Place: A-212